Table of Contents
Sufferers admitted to inpatient amenities are in peril for acute physiologic deterioration. This can result in extended hospitalization, admission to the ICU, or even cardiorespiratory arrest (1,2). Worsening in a affected person’s scientific situation ceaselessly stays undetected for hours previous to escalation of care (1). Makes an attempt at spotting deterioration early were advanced and vary from easy indicators in line with important signal alterations to pattern evaluation and sophisticated early caution rankings (EWS) (3). Those efforts were mixed with multidisciplinary fast reaction groups (RRTs) aimed toward well timed intervention and prevention of cardiorespiratory arrest (2). Owing in part to boundaries of the combination menace rankings and in part to variable RRT availability and composition, those efforts have no longer resulted in constant enhancements in results (4).
Well being knowledge generation (HIT) is widely outlined because the incorporation of more than a few knowledge assets, information, and generation to facilitate advanced conversation and decision-making (5). The in style implementation of digital scientific information (EMRs) has allowed get admission to to bigger amounts of scientific information and usage of prediction analytics (6). EMR-based alarms have emerged to reinforce well timed detection of acute stipulations equivalent to sepsis, acute kidney damage (AKI), and respiration failure (7–9). Virtual scientific resolution reinforce has additionally been created to lend a hand standardize the method and control of deteriorating sufferers (10).
Even if a up to date meta-analysis reported EMR advanced affected person protection via decreasing medicine mistakes and adversarial drug reactions, that learn about didn’t expose any growth in mortality (11). Any other meta-analysis eager about a huge vary of HIT within the inpatient environment and didn’t display aid in health facility mortality or duration of keep (LOS) both (12).
A lot paintings has been finished to expand techniques figuring out actionable deterioration when a affected person would possibly get pleasure from early consideration and motion from clinicians. Then again, affected person results from HIT supporting early detection of sufferers with actionable worsening stipulations stay unknown. The target of this systematic evaluation (SR) and meta-analysis used to be to judge the affect of HIT for early detection of affected person deterioration on affected person mortality and LOS within the acute care health facility environment. This systematic analysis would possibly lend a hand clinicians and establishments to make knowledgeable choices concerning the usage and implementation of HIT inside of procedure and workflow techniques throughout acute care scientific settings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The result of the learn about have been reported the usage of the Most well-liked Reporting Pieces for Systematic Evaluations and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statements (13) (Supplemental Desk 1, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H90). The Covidence device (Veritas Well being Innovation, Melbourne, Australia) used to be used for information assortment (14).
Information Resources and Seek Technique
A complete seek of a number of databases from 1990, when tough knowledge generation infrastructure in hospitals changed into extra in style, to January 19, 2021, used to be performed. The databases integrated MEDLINE and Epub Forward of Print, In-Procedure & Different Non-Listed Citations and Day-to-day, Embase, Cochrane Central Check in of Managed Trials, Cochrane Database of Systematic Evaluations, and Scopus. The quest technique used to be designed and performed via an skilled librarian with enter from learn about investigators. Managed vocabulary supplemented with key phrases used to be used to seek for research of passion. The real technique checklist all seek phrases used and the way they have been mixed is to be had in Supplemental Desk 2 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H91). The extra assets integrated grey literature seek and reference mining.
Find out about Variety
We integrated research that enrolled sufferers hospitalized on inpatient flooring, in ICU, or evaluated within the emergency division (ED). Eligible research assessed HIT for early detection of and notification about sufferers experiencing deterioration or at excessive menace of decay, as an intervention. Comparability teams won same old care in the similar learn about settings. Eligible research reported a minimum of one finish focal point: health facility LOS, ICU LOS, or mortality at any time level.
We excluded research that used an HIT intervention no longer detecting deterioration, and advanced or validated an HIT intervention handiest with out implementation into observe.
Titles, abstracts, and whole texts of recognized research have been independently reviewed via pairs of reviewers (S.H., Ok.L., Y.P., H.L., A.T., A.Ok.B.) the usage of prespecified eligibility standards. Disagreements have been resolved via a 3rd reviewer (S.H., V.H.) or via organization dialogue to achieve consensus.
Information Extraction
Find out about main points of integrated articles have been abstracted via two unbiased reviewers (Ok.L., Y.P., H.L., A.T.) the usage of a standardized information extraction shape. Further reviewers (S.H., A.Ok.B.) resolved disagreements. Information abstracted integrated learn about timeline, environment, inhabitants and dimension, intervention description, and results (Supplemental Appendix 1, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92).
End result Measures
The main consequence used to be distinction in health facility mortality between the intervention and comparability teams. The secondary results have been health facility LOS, ICU LOS, ICU mortality, and mortality at different recurrently reported time issues. All results have been prespecified.
Information Synthesis and Research
When imaginable, we extracted or calculated the percentages ratios (OR) and corresponding 95% CIs for binary results (mortality). We used adjusted OR when to be had. For steady results (LOS), we calculated imply variations (MDs) the usage of 95% CIs.
The DerSimonian and Laird random impact approach used to be used for quantitative synthesis of knowledge when a minimum of 3 eligible articles integrated the specified consequence. Meta-analyses have been carried out one by one for randomized managed trials (RCTs) and for pre-post research.
We evaluated heterogeneity between research the usage of the I2 statistics. I2 0–30% used to be categorised as low heterogeneity, 31–60% as average, and bigger than 60% as considerable heterogeneity (15).
To discover attainable assets of heterogeneity, we performed predetermined subgroup analyses in line with the learn about environment (ED, health facility flooring, or ICU), form of affected person deterioration recognized via HIT (sepsis, AKI, and others), and menace of bias (ROB).
We additionally performed publish hoc evaluation of RCTs to evaluate imaginable adjustments within the cumulative proof concerning the impact of HIT on health facility mortality over the years. Sensitivity analyses have been performed to evaluate robustness of the synthesized effects. Analyses have been carried out the usage of OpenMeta Analyst—an open-source, cross-platform device for complex meta-analysis (16). Two-tailed p worth of not up to 0.05 used to be thought to be statistically vital.
Possibility of Bias/High quality Evaluate
The ROB used to be assessed via Drs. Herasevich and Herasevich the usage of the Revised Cochrane ROB instrument for randomized trials (17) and The Possibility Of Bias In Nonrandomized Research—of Interventions overview instrument (18).
We evaluated the energy of proof the usage of Grading of Suggestions Evaluate, Building, and Analysis method (19). According to usual grading, analysis of RCTs used to be to start with thought to be as top of the range of proof and observational research as low high quality of proof. To evaluate attainable enhancing components affecting the energy of proof, we evaluated methodological boundaries of integrated research, precision, directness, consistency, and e-newsletter bias (19).
RESULTS
Find out about Variety
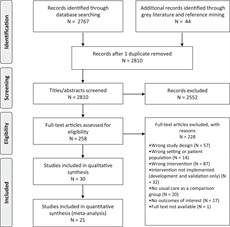
The quest technique recognized 2,767 research with 44 further research recognized via further searches (20). After casting off duplicates, 2,810 papers have been screened the usage of titles/abstracts. Following screening, 2,552 abstracts have been got rid of, and 258 papers remained for full-text evaluation. A few of the ultimate set of 30 research, 21 contained quantitative information and have been integrated within the meta-analyses for a number of results. See PRISMA diagram (Fig. 1) for learn about variety, levels, and causes for exclusion.

Most well-liked Reporting Pieces for Systematic Evaluations and Meta-Analyses float diagram.
Eligible Research and Player Traits
Supplemental Desk 3 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H93) summarizes the traits of the 30 eligible research. Many of the research have been performed in the US, six have been performed in Europe, and two in Asia. Twenty-three research have been unmarried heart, and 7 have been multicenter.
Eighteen research have been in line with health facility flooring (6,10,21–36) and 5 in ICU (37–41). Two research tested HIT implementation within the ED (42,43) after which analyzed results amongst the ones hospitalized following ED presentation. 5 research have been in line with each ICU and the health facility flooring (44–48).
Seven research have been RCTs, together with two cluster-randomized trials (22,41) and 5 in my view randomized trials (29,39,46–48). Twenty-three research used a pre- and a postimplementation design (6,10,21,23–28,30–38,40,42–45).
Seven research evaluated HIT for detection of AKI (21,32,37,38,46–48), 10 have been designed for early detection of sepsis or systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (10,24,25,27,33,35,39,42–44), and the rest 13 research for different forms of deterioration (6,22,23,26,28–31,34,36,40,41,45) equivalent to respiration or different physiologic deterioration. There used to be a loss of uniformity in how deterioration used to be quantified with some investigators the usage of rankings or standards for scientific syndromes and a few the usage of adjustments in important indicators, however all used tough approaches to outline deterioration (Supplemental Desk 4, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H94).
Baseline traits in intervention and comparability teams in integrated research have been equivalent. The median learn about length used to be 1.5 years with huge variation from 2.5 months to twelve years.
End result Measures
Some research assessed results of passion some of the complete learn about cohort, while different research handiest assessed the results amongst the ones sufferers assembly the standards for deterioration each in intervention and comparability teams. Thus, we performed two forms of meta-analyses: one comparing the mortality and health facility LOS for all integrated learn about sufferers (complete learn about cohort) and one comparing handiest the ones sufferers who reached the alert threshold outlined for each and every learn about and, due to this fact, detectable via the HIT.
All results for eligible research are summarized in Supplemental Desk 4 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H94). Then again, we restricted our evaluation to the principle and secondary results described above. We performed separate meta-analyses for RCTs and pre-post research for each and every consequence.
Possibility of Bias/High quality Appraisal
A few of the RCTs, the total ROB used to be low or average for many research because of loss of blinding amongst clinicians and consequence assessors (Supplemental Desk 5, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H95). Within the pre-post research, ROB used to be average or excessive for many research because of attainable confounding and incomplete reporting of research effects (Supplemental Desk 6, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H96).
Pooled impact dimension and high quality of proof for health facility mortality and LOS are reported in Supplemental Desk 7 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H97). The standard of proof of integrated research used to be low because of methodological boundaries, inconsistency, and imprecision.
Mortality
All integrated research assessed mortality as an consequence, even if at other time issues.
Health facility Mortality.
Twenty-eight of the 30 research (6,10,21–27,29–45,47,48) reported health facility mortality. 16 research assessing health facility mortality have been evaluated within the meta-analyses. Of those, 11 (6,30,31,34,37,39–41,43,45,47) reported health facility mortality for all the learn about cohort, two research (33,42) reported the result just for the ones sufferers assembly deterioration standards, and 3 (21,22,35) reported each.
Whole Cohort.
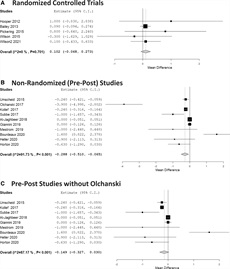
Within the meta-analysis of 4 RCTs, the implementation of HIT for early detection of affected person deterioration used to be no longer related to an important lower in health facility mortality (OR, 0.99 [95% CI, 0.80–1.21]) (Fig. 2).
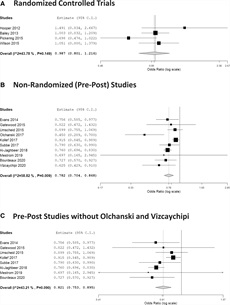
Meta-analyses on health facility mortality in sufferers who won the intervention (Well being Knowledge Generation for early detection of decay) when compared with same old care. Whole learn about cohort. A, Randomized managed trials. B, Nonrandomized (pre-post) research. C, Sensitivity evaluation of the pre-post research. The dimension of the knowledge markers represents the load each and every learn about has within the pooled end result.
Heterogeneity inside of this subset of research used to be average and will also be in part defined via the variation in forms of deterioration detected via HIT.
The meta-analysis of 10 pre-post research demonstrated an important affiliation between using HIT and advanced mortality (OR, 0.78 [95% CI, 0.70–0.87]) (Fig. 2). The heterogeneity used to be average on this organization and could also be attributed to the variation in forms of deterioration detected (Supplemental Fig. 1, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H98; legend, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92). Sensitivity evaluation demonstrated the stableness of the pooled impact dimension and just a marginal growth in heterogeneity (Fig. 2).
Find out about Members Assembly Standards for Deterioration.
Implementation of HIT used to be no longer related to a statistically vital lower in health facility mortality in 3 RCTs (22,29,48). Meta-analysis used to be no longer carried out as one learn about didn’t come with enough information.
Meta-analysis of 5 pre-post research demonstrated an important affiliation between HIT and a lower in health facility mortality (OR, 0.92 [95% CI, 0.87–0.97]) (Fig. 3). The heterogeneity inside of this subset used to be low.
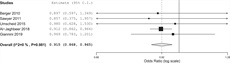
Meta-analysis on health facility mortality in sufferers who met the standards for deterioration amongst those that won the intervention (Well being Knowledge Generation for early detection of decay) when compared with same old care. Pre-post research. The dimension of the knowledge markers represents the load each and every learn about has within the pooled end result.
Further mortality results are reported in Supplemental Appendix 1 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92).
Health facility LOS
Twenty-three of the 30 integrated research assessed health facility LOS as an consequence (6,10,21–23,25–31,33–37,39–41,44,46,47). 16 research integrated quantitative information for analysis within the meta-analysis. Of those, 11 (26,27,30,31,34,37,39–41,46,47) reported the health facility LOS for all the learn about cohort, 3 research (23,29,33) reported the health facility LOS just for the ones sufferers who met the standards for deterioration, and 4 (21,22,25,35) reported each.
Whole Cohort
Within the meta-analysis of 5 RCTs, no vital distinction in health facility LOS used to be discovered (MD, 0.10 [95% CI, –0.07 to 0.27]) (Fig. 4). The heterogeneity used to be low on this organization of research.
Meta-analyses on health facility duration of keep in sufferers who won the intervention (Well being Knowledge Generation for early detection of decay) when compared with same old care. Whole learn about cohort. A, Randomized managed trials. B, Nonrandomized (pre-post) research. C, Sensitivity evaluation of the pre-post research. The dimension of the knowledge markers represents the load each and every learn about has within the pooled end result.
Meta-analysis of 10 pre-post research demonstrated vital affiliation of HIT with diminished LOS (MD, –0.29 [95% CI, –0.51 to –0.07]) (Fig. 4). Then again, the heterogeneity on this set of research used to be considerable and may just no longer be totally defined via distinction in ROB, learn about settings, or forms of detected deterioration (Supplemental Fig. 2, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H99; legend, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92). One glaring outlier, Olchanski et al (40), when compared two cohorts with time distinction in 4 years, and its effects have been most likely suffering from the observe adjustments over the years. Sensitivity evaluation confirmed that following elimination of this learn about, no vital affiliation between HIT and growth in health facility LOS used to be demonstrated (MD, –0.15 [95% CI, –0.33 to 0.03]) (Fig. 4).
Find out about Members Assembly Standards for Deterioration.
Two RCTs comparing health facility LOS amongst sufferers assembly standards for deterioration (22,29) didn’t display vital growth in LOS.
Then again, within the meta-analysis of 4 pre-post research, HIT implementation used to be related to an important aid in health facility LOS (MD, –0.29 [95% CI, –0.48 to –0.11]) (Fig. 5).

Meta-analysis on health facility duration of keep in sufferers who met the standards for deterioration amongst those that won the intervention (Well being Knowledge Generation for early detection of decay) when compared with same old care. Pre-post research. The dimension of the knowledge markers represents the load each and every learn about has within the pooled end result.
Further LOS results are reported in Supplemental Appendix 1 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92), Supplemental Determine 3 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H100; legend, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92), and Supplemental Determine 4 (https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H101; legend, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H92).
DISCUSSION
On this SR and meta-analyses, we evaluated the affect of HIT for early detection of affected person physiologic deterioration on health facility mortality and LOS. We integrated 30 research assessing sufferers in acute care health facility settings. There used to be variability in environment, interventions, form of deterioration detected, and consequence dimension approaches. We performed a couple of analyses to check equivalent learn about designs and teams with equivalent consequence approaches (research reporting results for complete learn about cohorts and just for sufferers assembly deterioration standards).
We discovered that HIT for early detection of affected person deterioration used to be no longer related to a discount in health facility mortality or LOS within the RCTs and related meta-analyses. Within the meta-analyses of pre-post research, HIT intervention used to be considerably related to advanced health facility mortality and health facility LOS. ICU LOS didn’t exchange considerably with HIT interventions. LOS is usually a difficult consequence measure because of competing menace of mortality and the opportunity of together with the ones with a brief survival time who’ve died (49).
There were a number of SRs and meta-analyses exploring the affects of HIT on affected person results. Then again, the ones research differed from our learn about in numerous tactics. The learn about via Varghese et al (50) eager about automatic resolution reinforce gadget (DSS) implementations and located sure however no longer clinically essential enhancements in affected person results. That learn about famous a loss of rigorous RCTs to evaluate scientific resolution reinforce. The SR via Despins (51) eager about detection of sepsis handiest and famous that present efficiency variability affected the affect on affected person results. Two extra SRs have eager about a huge vary of HIT together with EMR, DSS, automatic doctor order access, and surveillance techniques (“sniffers”) and feature no longer demonstrated enhancements in health facility mortality or LOS (11,12). By contrast to different SRs, we targeted at the subset of HIT in particular designed for early detection of decay that were applied in acute care settings.
A notable discovering of our paintings total is the variation between the conclusions of the RCTs and the pre-post research. HIT implementation used to be no longer related to enhancements in health facility mortality within the RCTs which can be thought to be the gold usual of study and a rigorous solution to keep away from confounding (52). The research supporting using HIT have been most often pre-post research, and the conclusions from those research want to be thought to be in moderation because of the excessive chance of confounding defined underneath.
We recognized a number of classes of attainable cofounders that can have performed a very powerful position within the advanced results within the pre-post research in our SR. Those have been: 1) coaching and training of body of workers (6,37), 2) huge high quality growth tasks wherein the HIT used to be only one element (10,23,43), 3) exchange control exams and normal enhancements over the years (30,35,40,45), 4) complicated multicomponent or multifaceted interventions that still integrated DSS and dashboards (40,45), and 5) the Hawthorne impact (10,23,34,37,53).
Even if research ceaselessly reported that there have been no recognized vital adjustments within the scientific observe all the way through the learn about duration, they have been most likely nonetheless susceptible to bias and influenced via time and total enhancements in observe. As an example, one of the crucial two research demonstrating the perfect advantage of HIT on health facility mortality (45) evaluated COVID sufferers early in pandemic, and it’s most likely that growth in mortality used to be because of advances in COVID affected person control slightly than to HIT implementation (54). Any other learn about when compared a postimplementation cohort with ancient controls from 4 years previous to implementation (40).
No doubt, the mechanism in which HIT used to be built-in to the clinicians’ workflow is essential. Then again, equivalent approaches to HIT integration would possibly yield other effects. Six research on this SR evaluated HIT implementation to complement RRT activations in settings the place RRT activations have been the usual of care. Of the ones, 3 pre-post research demonstrated a lower in health facility mortality related to HIT intervention (23,30,34). Imaginable components related to the sure impact on health facility mortality integrated off-site nurse evaluation to clear out indicators ahead of contacting the RRT, alerting bedside body of workers in addition to RRT participants, and possible enhancements in observe over a protracted learn about duration. The opposite 3 research (two pre-post research that evaluated sepsis-related results, and one RCT) didn’t display any vital growth in health facility mortality (24,29,35).
Our SR has a number of strengths. We carried out meta-analyses of research reporting significant affected person results: LOS and mortality, slightly than extra in an instant and simply measurable surrogate markers equivalent to time to RRT activation, ICU switch, or explicit interventions, which helped us shape tough conclusions (55). Find out about settings integrated all related acute care health facility populations: flooring, ICU, and ED, and maximum research have been massive. We handiest integrated research assessing HIT that were applied in observe versus research that described building or validation of an HIT to evaluate “real-world” use of HIT and its results on affected person results (41). Even if our SR features a huge vary of settings and populations, we was hoping this paintings would supply related insights around the spectrum of acute care.
Essential boundaries are as follows. Heterogeneity used to be discovered to be average or considerable within the meta-analyses of the research comparing health facility mortality, health facility, and ICU LOS some of the complete learn about cohorts (Figs. 2 and four; Supplemental Fig. 1, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H98; Supplemental Fig. 2, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H99; Supp lemental Fig. 3, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H100; Supplemental Fig. 4, https://hyperlinks.lww.com/CCM/H101 [legend, https://links.lww.com/CCM/H92]). This heterogeneity used to be most commonly attributed to the variation in forms of deterioration detected and learn about flaws associated with temporal and observe adjustments. HIT for the detection of affected person deterioration integrated distinct forms of digital techniques the usage of information from steady bedside tracking, EMR, and different digital documentation. There used to be no longer a uniform definition of standards for scientific deterioration throughout all research. The commonest stipulations recognized have been AKI, early sepsis, or physiologic deterioration in line with EWS or important indicators parameters. The adaptation in baseline states and requirements of care throughout learn about settings might also impact the impact of HIT implementation.
Then again, even if form of deterioration, modality of overview, and illness states differed, all HIT implementation mechanisms required emergent responses via the scientific staff as an integral a part of the intervention and have been designed to alert the groups to deterioration previous than same old observe.
The knowledge of proof of the integrated research used to be low, most commonly because of methodological boundaries and inconsistency. Some research described unadjusted effects, and a few effects have been obscure together with huge CIs. Subsequently, it’s imaginable that different unmeasured components influenced the effectiveness of the intervention, probably under- or overestimating the actual affect.
Progressed effects after HIT implementation within the pre-post research could also be attributed extra to observe advances and high quality growth projects slightly than to HIT implementation itself.
CONCLUSIONS
On this SR and meta-analysis, the implementation of HIT for early detection of decay in acute care settings used to be no longer considerably related to advanced mortality or LOS within the meta-analyses of RCTs. Within the meta-analyses of pre-post research, HIT used to be related to growth in health facility mortality and health facility LOS; alternatively, those effects must be interpreted with warning. We consider the variations in affected person results between the findings of the RCTs, and pre-post research could also be secondary to a couple of attainable confounding components together with observe advances and high quality growth projects slightly than to HIT implementation itself.
REFERENCES